1. What is a Primary Key?
A primary key is a single column or multiple columns defined to have unique values that can be used as row identifications
2. What is a Foreign Key?
A foreign key is a single column or a multiple columns defined to have values that can be mapped to a primary key in another table.
3. What is an Index?
An index is a single column or multiple columns defined to have values pre-sorted to speed up data retrieval speed.
4. What are NULL values?
NULL represents no value
NULL is not the same as an empty string ‘’
NULL is not same as zero value (0)
NULL can be used as any data type
NULL should not be used in any comparison operators
NULL has its own equality operator IS and not-equality operator IS NOT
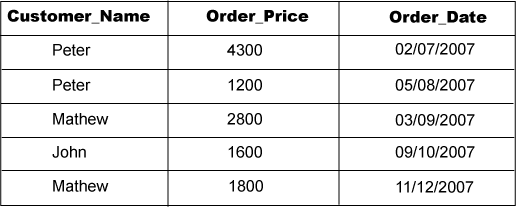
5. Write a query to find the 5th details from a table
SELECT column_name FROM table_name WHERE auto_incremented_id =
(SELECT TOP 1 auto_incremented_id FROM
(SELECT TOP 3 auto_incremented_id FROM employee ORDER BY auto_incremented_id ASC)
table_name ORDER BY auto_incremented_id DESC);
6. Write a Query to display the Top N rows ?
MySQL
SELECT column_name FROM table_name
LIMIT number
SQL Server
SELECT TOP number/percent column_name FROM table_name
Oracle
SELECT column_name FROM table_name
WHERE ROWNUM<= number
7. Write a Query to display the Last N rows ?
MySQL
SELECT column_name FROM table_name
ORDER BY auto_incremented_id DESC
LIMIT number
SQL Server
SELECT TOP number/percent column_name
FROM table_name
ORDER BY auto_incremented_id DESC
Note: The above query will display the result in descending order
To display the result in ascending order
SELECT * FROM (SELECT TOP number/percent column_name
FROM table_name
ORDER BY auto_incremented_id DESC)
ORDER BY auto_incremented_id ASC
ORACLE
SELECT * FROM (SELECT column_name FROM table_name
ORDER BY auto_incremented_id DESC)
WHERE ROWNUM<= number
ORDER BY auto_incremented_id ASC
8. Write a Query to display the second highest salary ?
SELECT
MAX (empsal) FROM employee
WHERE empsal < (
SELECT
MAX (empsal) FROM employee)
Explanation:
First the subquery will be executed. i.e. SELECT
MAX (empsal) FROM employee) = 20000
Then the main query will be executed i.e.
SELECT
MAX (empsal) FROM employee
WHERE empsal < 20000 = 15000
9. Write a query to retrieve the duplicate rows in a table ?
SELECT empname, empsal FROM employee
GROUP BY empname, empsal
HAVING count(*) > 1
10. What is RDBMS?
Relational Data Base Management Systems (RDBMS) that maintains data records and indices in tables. Relationships may be created and maintained across and among the data and tables.
11. What is SQL?
SQL stands for 'Structured Query Language', developed by IBM in 1970’s
12. What is SELECT statement?
The SELECT statement lets you select a set of values from a table in a database. The values selected from the database table would depend on the various conditions that are specified in the SQL query.
13. What is normalization?
Database normalization is a data design and organization process applied to data structures based on rules that help build relational databases.
14. What is the INSERT statement?
The INSERT statement allows us to insert information into a database.
15. How do you delete a record from a database?
Using the DELETE statement we can remove records or any particular column values from a database.
16. How to find the total number of records in a database table?
We can use the COUNT keyword for counting records,
Example: SELECT COUNT(*) FROM Emp
17. What is View?
A simple view can be thought of as a subset of a table. It can be used for retrieving data, as well as updating or deleting rows.
18. What is Index?
An index is a physical structure containing pointers to the data. Indices are created in an existing table to locate rows more quickly and efficiently.
19. What is GROUP BY?
GROUP BY keyword has been added to SQL because aggregate functions (like SUM) return the aggregate of all column values every time they are called. Without the GROUP BY functionality, finding the sum for each individual group of column values was not possible.
20. What is the difference among "dropping a table", "truncating a table" and "deleting all records" from a table?
Dropping: (Table structure + Data are deleted), Invalidates the dependent objects, Drops the indexes
Truncating: (Data alone deleted), Performs an automatic commit, Faster than delete
Delete: (Data alone deleted), Doesn’t perform automatic commit
21. What's the difference between a primary key and a unique key?
Both primary key and unique enforce uniqueness of the column on which they are defined. But by default primary key creates a clustered index on the column, where are unique creates a nonclustered index by default.
Another major difference is that, primary key doesn't allow NULLs, but unique key allows one NULL only.
22. What are triggers? How to invoke a trigger on demand?
Triggers are special kind of stored procedures that get executed automatically when an INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE operation takes place on a table.
Triggers can't be invoked on demand. They get triggered only when an associated action (INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) happens on the table on which they are defined.
23. What is a join and explain different types of joins?
Join is used in queries to explain how different tables are related. Joins also let us select data from a table depending upon data from another table.
Types of joins:
INNER JOINs, OUTER JOINs, CROSS JOINs.
Note: OUTER JOINs are further classified as LEFT OUTER JOINS, RIGHT OUTER JOINS and FULL OUTER JOINS.
24. What is a self join?
Self join is just like any other join, except that two instances of the same table will be joined in the query.
25. How to implement one-to-one, one-to-many and
many-to-many relationships while designing tables?
One-to-One relationship can be implemented as a single table and rarely as two tables with primary and foreign key relationships.
One-to-Many relationships are implemented by splitting the data into two tables with primary key and foreign key relationships.
Many-to-Many relationships are implemented using a junction table with the keys from both the tables forming the composite primary key of the junction table.
26. What are the Properties of Sub-Query?
A sub query must be enclosed in the parenthesis.
A sub query must be put in the right hand of the comparison operator, and
A sub query cannot contain a ORDER-BY clause.
A query can contain more than one sub-queries.
27. What are types of sub-queries?
Single-row sub query, where the sub query returns only one row.
Multiple-row sub query, where the sub query returns multiple rows,.
Multiple column sub query, where the sub query returns multiple columns.
28. What are the different index configurations a table can have?
A table can have one of the following index configurations:
a) No indexes
b) A clustered index
c) A clustered index and many nonclustered indexes
d) A nonclustered index
e) Many nonclustered indexes
29. What is the difference between a Local and a Global temporary table?
A local temporary table exists only for the duration of a connection or, if defined inside a compound statement, for the duration of the compound statement.
A global temporary table remains in the database permanently, but the rows exist only within a given connection. When connection is closed, the data in the global temporary table disappears. However, the table definition remains with the database for access when database is opened next time.